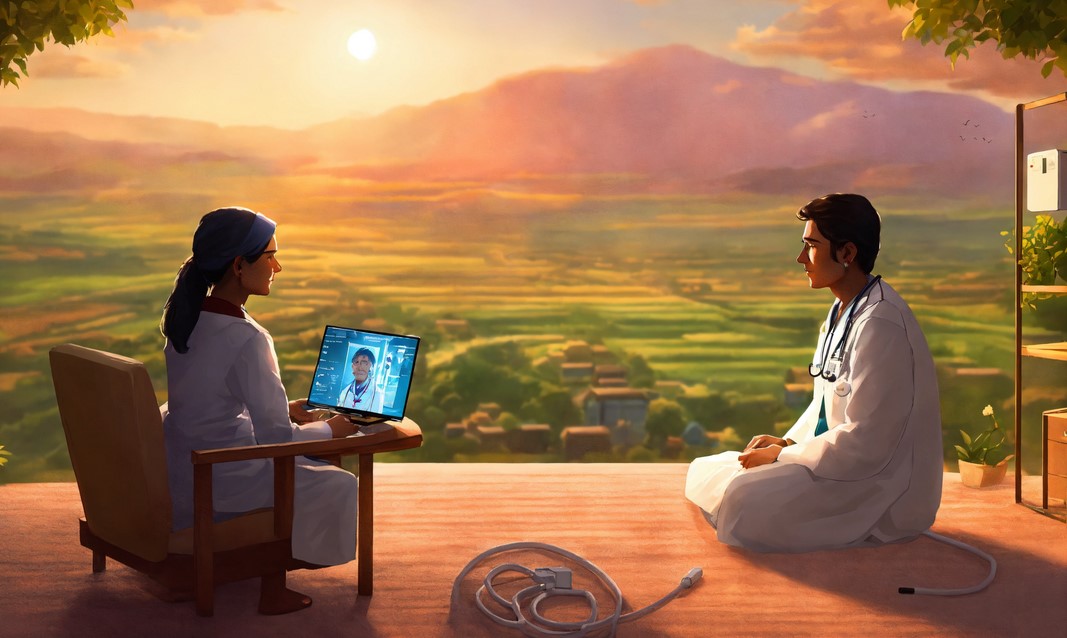
In recent years, telehealth has emerged as a critical component of modern healthcare, revolutionizing the way patients access medical services and how providers deliver care. The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated the adoption of telehealth, demonstrating its potential to enhance healthcare accessibility, efficiency, and patient outcomes. This article explores the key aspects of telehealth, its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Telehealth:
Definition and Scope:
Telehealth vs. Telemedicine: While telemedicine specifically refers to remote clinical services, telehealth encompasses a broader range of services, including remote non-clinical services, provider training, administrative meetings, and continuing medical education.
Modes of Delivery: Telehealth can be delivered through various means, including live video conferencing, remote patient monitoring, mobile health apps, and secure messaging platforms.
Technological Components:
Video Conferencing: Real-time video consultations enable patients to connect with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes, facilitating timely medical advice and follow-ups.
Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and sensors allow continuous monitoring of patients’ vital signs, enabling early detection of potential health issues and reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
Mobile Health Applications: Health apps provide tools for self-monitoring, medication reminders, appointment scheduling, and access to medical records, empowering patients to manage their health proactively.
Benefits of Telehealth:
Increased Accessibility:
Geographic Barriers: Telehealth bridges the gap for patients in rural or remote areas who have limited access to healthcare facilities, providing them with timely medical consultations and reducing travel-related burdens.
Specialist Access: Telehealth facilitates access to specialists, particularly for patients with complex or rare conditions, ensuring they receive expert advice without the need for long-distance travel.
Convenience and Efficiency:
Reduced Wait Times: Virtual consultations can often be scheduled more quickly than in-person appointments, reducing wait times and enabling prompt medical attention.
Flexible Scheduling: Telehealth offers flexible scheduling options, accommodating patients’ busy lifestyles and reducing the need to take time off work or arrange childcare for in-person visits.
Enhanced Chronic Disease Management:
Continuous Monitoring: Remote monitoring devices provide real-time data on patients’ health status, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions and adjust treatment plans promptly.
Patient Engagement: Telehealth encourages active patient participation in managing chronic conditions, leading to better adherence to treatment plans and improved health outcomes.
Cost Savings:
Reduced Healthcare Costs: Telehealth can lower healthcare costs by reducing hospital readmissions, emergency room visits, and the need for in-person consultations.
Patient Savings: Patients save on travel expenses, time off work, and other costs associated with in-person visits.
Challenges in Telehealth Implementation:
Technological Barriers:
Internet Access: Reliable high-speed internet access is crucial for effective telehealth services. Patients in underserved areas may face challenges due to limited internet connectivity.
Digital Literacy: Patients and providers need to be comfortable with using digital devices and telehealth platforms. Lack of digital literacy can hinder the adoption and effectiveness of telehealth services.
Privacy and Security:
Data Protection: Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is paramount. Telehealth platforms must comply with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to safeguard sensitive health information.
Cybersecurity: Telehealth systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity measures are necessary to protect patient data and maintain trust in telehealth services.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues:
Licensing and Regulations: Telehealth providers must navigate complex licensing requirements and regulations that vary by state and country, which can pose challenges to cross-border telehealth services.
Reimbursement Policies: Insurance reimbursement policies for telehealth services are evolving. Ensuring fair and consistent reimbursement for telehealth consultations is crucial for its sustainability.
Quality of Care:
Clinical Limitations: Certain medical conditions may require physical examinations or diagnostic tests that cannot be performed virtually. Identifying appropriate use cases for telehealth is essential to maintain the quality of care.
Provider-Patient Relationship: Building a strong provider-patient relationship in a virtual setting can be challenging. Ensuring effective communication and patient engagement is key to successful telehealth interactions.
Future Prospects of Telehealth:
Integration with Traditional Healthcare:
Hybrid Models: Combining telehealth with traditional in-person care can create a hybrid model that leverages the strengths of both approaches. This model can enhance care coordination and provide a comprehensive healthcare experience.
Patient-Centered Care: Telehealth can support patient-centered care by providing personalized and convenient healthcare solutions tailored to individual needs.
Advancements in Technology:
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered telehealth solutions can enhance diagnostic accuracy, predict patient outcomes, and provide decision support to healthcare providers.
Wearable Technology: Advances in wearable devices and sensors will enable more sophisticated remote monitoring and real-time health data collection.
Global Health Impact:
Telehealth in Developing Countries: Telehealth can play a crucial role in improving healthcare access and outcomes in developing countries with limited healthcare infrastructure.
Pandemic Preparedness: Telehealth can enhance pandemic preparedness and response by providing remote medical consultations, reducing the burden on healthcare facilities, and minimizing the risk of infection transmission.
Embracing Telehealth for a Healthier Future
Telehealth is transforming healthcare delivery by making medical services more accessible, convenient, and efficient. While challenges remain, ongoing technological advancements and evolving regulatory frameworks are paving the way for the widespread adoption of telehealth. Embracing telehealth as a complement to traditional healthcare can lead to improved patient outcomes, enhanced chronic disease management, and cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems.